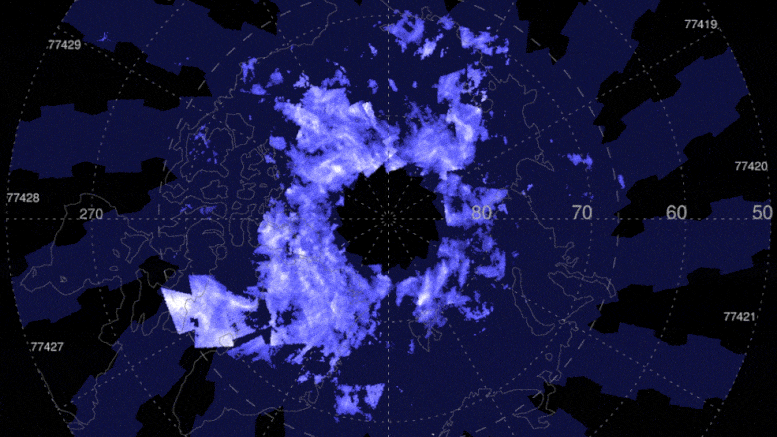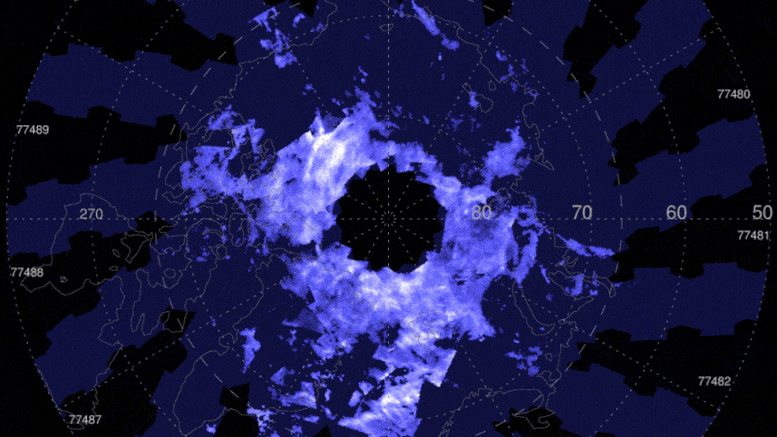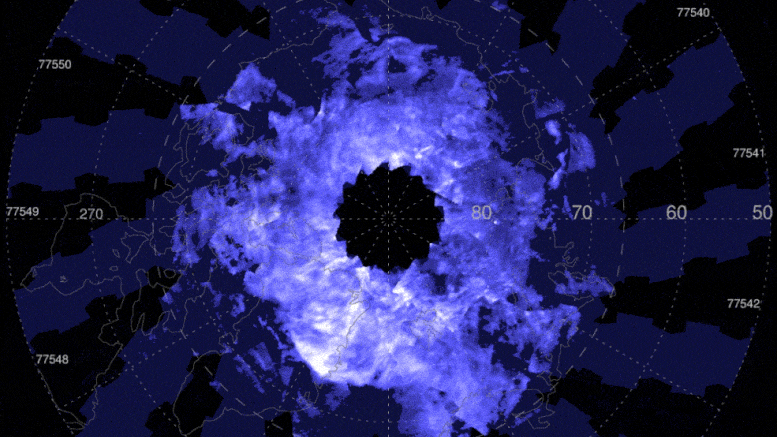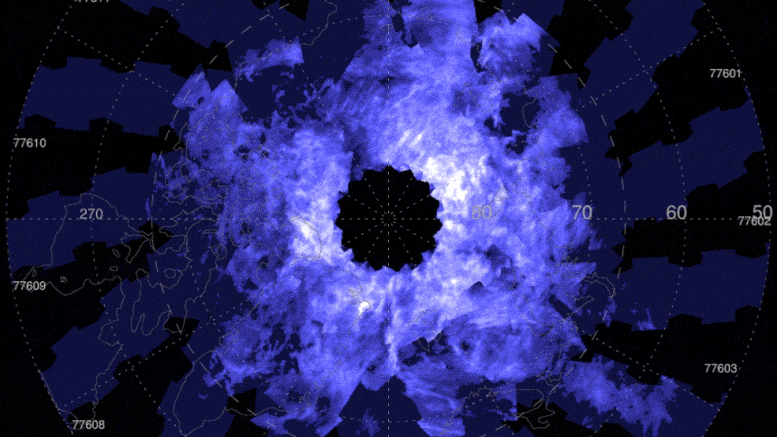
These AIM images cover June 6-June 18, 2021, when the Northern Hemisphere noctilucent cloud season was well underway. The colors– from dark blue to light blue and bright white– suggest the clouds albedo, which refers to the quantity of light that a surface shows compared to the total sunlight that falls upon it.
Considering that the mesosphere is much thinner than the part of the environment we reside in, the impacts of increasing greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, vary from the warming we experience at the surface area. One researcher compared where we live, the troposphere, to a thick quilt.
” Down near Earths surface, the atmosphere is thick,” said James Russell, a research study co-author and climatic researcher at Hampton University in Virginia. “Carbon dioxide traps heat similar to a quilt traps your body heat and keeps you warm.” In the lower atmosphere, there are plenty of particles in close proximity, and they quickly trap and transfer Earths heat in between each other, keeping that quilt-like heat.
That indicates little of Earths heat makes it to the greater, thinner mesosphere. There, molecules are scarce. Since co2 likewise effectively emits heat, any heat recorded by co2 earlier escapes to area than it discovers another molecule to absorb it. As an outcome, a boost in greenhouses gases like carbon dioxide indicates more heat is lost to area– and the upper environment cools. When air cools, it contracts, the very same way a balloon diminishes if you put it in the freezer.
This cooling and contracting didnt come as a surprise. For many years, “designs have been revealing this effect,” said Brentha Thurairajah, a Virginia Tech atmospheric researcher who added to the research study. “It would have been weirder if our analysis of the information didnt reveal this.”
While previous research studies have actually observed this cooling, none have used a data record of this length or shown the upper environment contracting. The researchers say these brand-new outcomes improve their confidence in our ability to design the upper environments complicated changes.
At many altitudes, the mesosphere cooled as carbon dioxide increased. In other words, the mesosphere was contracting.
Earths Middle Atmosphere
What takes place in the mesosphere does not straight effect humans, the area is an essential one. The upper boundary of the mesosphere, about 50 miles above Earth, is where the coolest climatic temperature levels are found. Its also where the neutral environment begins transitioning to the tenuous, electrically charged gases of the ionosphere.
Even greater up, 150 miles above the surface area, climatic gases trigger satellite drag, the friction that tugs satellites out of orbit. Satellite drag also assists clear area scrap. When the mesosphere agreements, the remainder of the upper atmosphere above sinks with it. As the environment agreements, satellite drag might wane– interfering less with running satellites, but likewise leaving more area junk in low-Earth orbit.
This infographic details the layers of Earths atmosphere. Click to explore in full size. Credit: NASA
The mesosphere is also known for its dazzling blue ice clouds. Theyre called polar or noctilucent mesospheric clouds, so named due to the fact that they live in the mesosphere and tend to huddle around the North and South Poles. The clouds form in summertime, when the mesosphere has all 3 components to produce the clouds: water vapor, very cold temperature levels, and dust from meteors that burn up in this part of the environment. Noctilucent clouds were identified over northern Canada on May 20, starting the start of the Northern Hemispheres noctilucent cloud season.
Theyre a helpful signal of change in the mesosphere since the clouds are sensitive to temperature and water vapor. “We understand the physics of these clouds,” Bailey stated. In current decades, the clouds have drawn researchers attention because theyre acting unusually. Theyre getting brighter, wandering further from the poles, and appearing earlier than typical. And, there seem to be more of them than in years past.
“The only way you would anticipate them to change this method is if the temperature is getting colder and water vapor is increasing,” Russell said. Chillier temperature levels and abundant water vapor are both related to climate change in the upper environment.
Currently, Russell functions as primary detective for AIM, brief for Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, the newest satellite of the three that contributed data to the study. Russell has served as a leader on all three NASA missions: AIM, the instrument SABER on TIMED (Thermosphere, Ionosphere, Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics), and the instrument HALOE on the since-retired UARS (Upper Atmospherics Research Satellite).
TIMED and AIM launched in 2001 and 2007, respectively, and both are still operating. The UARS objective ran from 1991 to 2005. “I always had in my mind that we would have the ability to put them together in a long-lasting modification study,” Russell said. The research study, he stated, shows the importance of long-lasting, space-based observations across the world.
In the future, the researchers expect more striking display screens of noctilucent clouds that wander off further from the poles. Since this analysis concentrated on the poles at summer, Bailey said he plans to analyze these effects over longer amount of times and– following the clouds– study a wider stretch of the environment.
The colors– from dark blue to light blue and bright white– suggest the clouds albedo, which refers to the amount of light that a surface area shows compared to the overall sunlight that falls upon it. The mesosphere is also understood for its fantastic blue ice clouds. The clouds form in summertime, when the mesosphere has all 3 active ingredients to produce the clouds: water vapor, extremely cold temperature levels, and dust from meteors that burn up in this part of the atmosphere. Noctilucent clouds were spotted over northern Canada on May 20, kicking off the start of the Northern Hemispheres noctilucent cloud season.
Due to the fact that the clouds are sensitive to temperature level and water vapor, theyre a helpful signal of change in the mesosphere.